What is prostate cancer?
The prostate is a walnut-sized exocrine gland. This means that its fluids and secretions are intended for use outside of the body.
The prostate produces the fluid that nourishes and transports sperm on their journey to fuse with a female ovum, or egg, and produce human life. The prostate contracts and forces these fluids out during orgasm.
 The protein excreted by the prostate, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), helps semen retain its liquid state. An excess of this protein in the blood is one of the first signs of prostate cancer.
The protein excreted by the prostate, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), helps semen retain its liquid state. An excess of this protein in the blood is one of the first signs of prostate cancer.
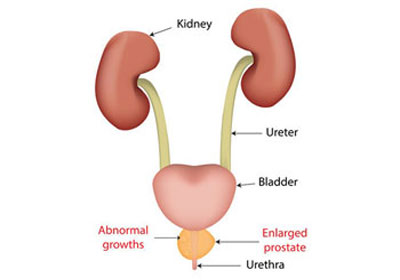
The urethra is tube through which sperm and urine exit the body. It also passes through the prostate.
As such, the prostate is also responsible for urine control. It can tighten and restrict the flow of urine through the urethra using thousands of tiny muscle fibers.
How does it start?
It usually starts in the glandular cells. This is known as adenocarcinoma. Tiny changes occur in the shape and size of the prostate gland cells, known as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN). This tends to happen slowly and does not show symptoms until further into the progression.
Nearly 50 percent of all men over the age of 50 years have PIN. High-grade PIN is considered pre-cancerous, and it requires further investigation. Low-grade PIN is not a cause for concern.
Prostate cancer can be successfully treated if it is diagnosed before metastasis, but if it spreads, it is more dangerous. It most commonly spreads to the bones.
Symptoms
There are usually no symptoms during the early stages of prostate cancer.
If symptoms appear, they usually involve one or more of the following:
- frequent urges to urinate, including at night
- difficulty commencing and maintaining urination
- blood in the urine
- painful urination and, less commonly, ejaculation
- difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection may be difficult
Advanced prostate cancer can involve the following symptoms:
- bone pain, often in the spine, femur, pelvis, or ribs
- bone fractures
If the cancer spreads to the spine and compresses the spinal cord, there may be:
- leg weakness
- urinary incontinence
- fecal incontinence
Treatment
Treatment is different for early and advanced prostate cancers.
Early stage prostate cancer
If the cancer is small and localized, it is usually managed by one of the following treatments:
Watchful waiting or monitoring: PSA blood levels are regularly checked, but there is no immediate action. The risk of side-effects sometimes outweighs the need for immediate treatment for this slow-developing cancer.
Radical prostatectomy: The prostate is surgically removed. Traditional surgery requires a hospital stay of up to 10 days, with a recovery time of up to 3 months. Robotic keyhole surgery involves a shorter hospitalization and recovery period, but it can be more expensive. Patients should speak to their insurer about coverage.
Brachytherapy: Radioactive seeds are implanted into the prostate to deliver targeted radiation treatment.
Conformal radiation therapy: Radiation beams are shaped so that the region where they overlap is as close to the same shape as the organ or region that requires treatment. This minimizes healthy tissue exposure to radiation.
Intensity modulated radiation therapy: Beams with variable intensity are used. This is an advanced form of conformal radiation therapy.
In the early stages, patients may receive radiation therapy combined with hormone therapy for 4 to 6 months.
Treatment recommendations depend on individual cases. The patient should discuss all available options with their urologist or oncologist.